Frequently Asked Questions:
Brain Aneurysms
What is a brain aneurysm?
A brain aneurysm is a saccular bulge that develops on the side wall of an artery. It develops due to a weakness in the artery wall, and this grows into an aneurysm. Usually, an aneurysm forms at the bifurcation, or split, as one artery gives off a branch. There are several kinds of aneurysms, but the most common is the saccular aneurysm.
This sounds very scary. Is this an emergency?
Being diagnosed with a brain aneurysm is scary and you should be seen by an expert to review this in person. But if an aneurysm has not had any bleeding, then it is not an emergency and you can make an appointment to see a cerebrovascular neurosurgeon when you get diagnosed.
I was told I have a “ticking time bomb”, is this true?
The main risk of a brain aneurysm is that it could bleed. If an aneurysm bleeds this certainly can lead to brain injury and even death. But there is some good news. Most brain aneurysms have a relatively low risk of bleeding and some don’t even need treatment at all. So I prefer not to use the term “ticking time bomb” as it unnecessarily creates anxiety.
What is the risk of my aneurysm bleeding?
…Well that depends. Many articles looking at the natural history of brain aneurysms have been published and provide excellent data for risk of bleeding. I use this data to give you a sense of the risk of bleeding from your aneurysm. This is vital to decide if you need treatment. The risk of aneurysm bleeding depends on two main factors – size and location. Depending on these factors, we can give you an estimate of the risk of bleeding in the future. Some other factors can influence risk of bleeding including smoking and hypertension.
Do all brain aneurysms need treatment?
Although it seems they should, some aneurysms don’t need treatment at all. If your aneurysm has a very low risk of bleeding, then treatment might not be needed. In this case, we could simply watch it to make sure it doesn’t grow over time.
What is the treatment for brain aneurysms?
There are two main types of treatments to fix brain aneurysms – 1) Surgical and 2) Endovascular. Surgical treatment has been around the longest and was the primary form of aneurysm treatment until about 15 years ago. Surgery is what most people imagine as a “brain surgery” and requires a cerebrovascular surgeon to place a clip on the aneurysm.
The other treatment is Endovascular. As technology has improved over the last 20 years, devices that can navigate through the blood vessels can be used to treat aneurysms. Like cardiologists put in heart stents, physicians trained in Endovascular Neurological Surgery can treat aneurysms by going through the artery in the leg.
Can you explain surgery for brain aneurysms?
Surgery for brain aneurysms requires an incision on the scalp and then a tailored approach around the brain to treat your aneurysm. For treating aneurysms, we don’t have to go through the brain, but rather we go around the brain since the blood vessels that have aneurysms lie on the surface.
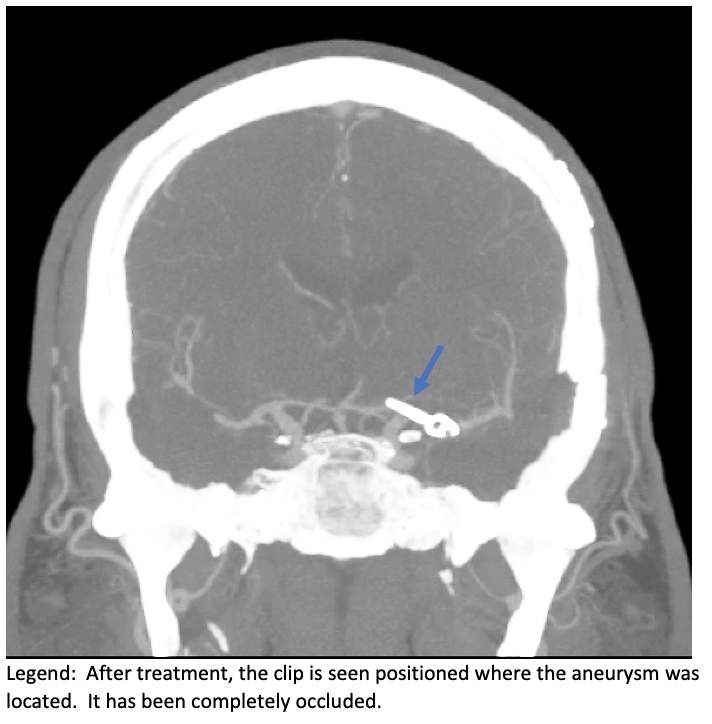
Once we find the aneurysm, we can place an aneurysm clip and occlude the aneurysm. This makes it so that no blood goes in the aneurysm. This treatment is very durable and is often curative.
Can you explain Endovascular treatment for brain aneurysms?
This is a treatment entirely inside the blood vessels. It does not require a skin incision on the scalp or any brain dissection. The access is through the femoral artery, an artery in the groin. Through this artery, we can go up to the brain using small catheters and treat the aneurysm.
There are several types of endovascular options, but the most common treatment is coil embolization. This means that you fill the sack of the aneurysm with small metal coils. If you can fill it sufficiently with coils, then this means blood doesn’t circulate in the aneurysm and the aneurysm is treated.
I have heard of other endovascular treatments like flow diversion and intrasaccular devices. Are these good options?
The technology for treatment of brain aneurysms continues to advance and these are newer devices that have been approved for aneurysm treatment. The best treatment for your aneurysm typically depends on location and the anatomy of the aneurysm. My personal practice continues to evolve with the newer devices and I use these when I think they are the best option.